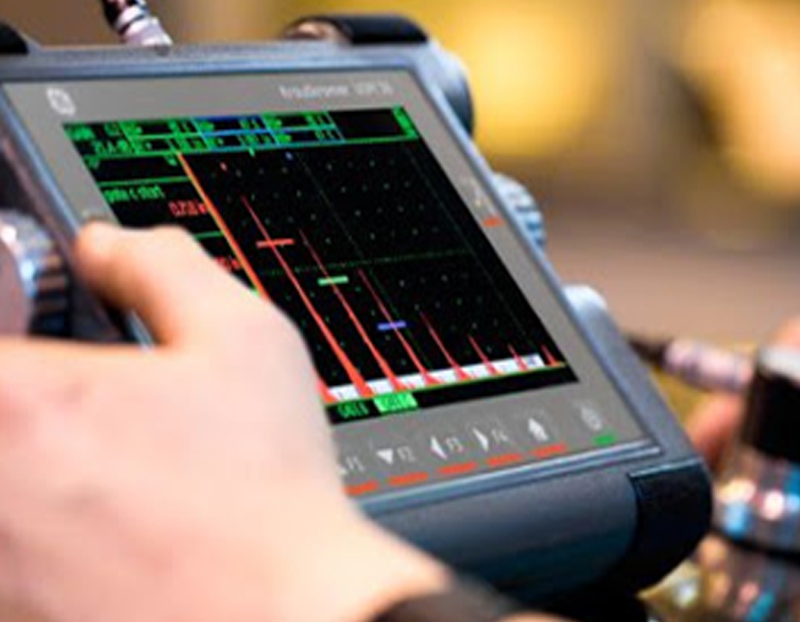

Ultrasonic Inspection (UT) is a non-destructive testing method that uses high frequency sound waves to inspect the internal structure of materials for defects or variations in thickness. The technique works by transmitting ultrasonic waves into the material and measuring the time it takes for the waves to reflect back from any internal imperfections. UT is commonly used to inspect metal components in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and power generation for quality control and safety purposes. We are equipped with state of art digital flaw detectors and our technicians are well qualified, certified for reliable & faster inspection.
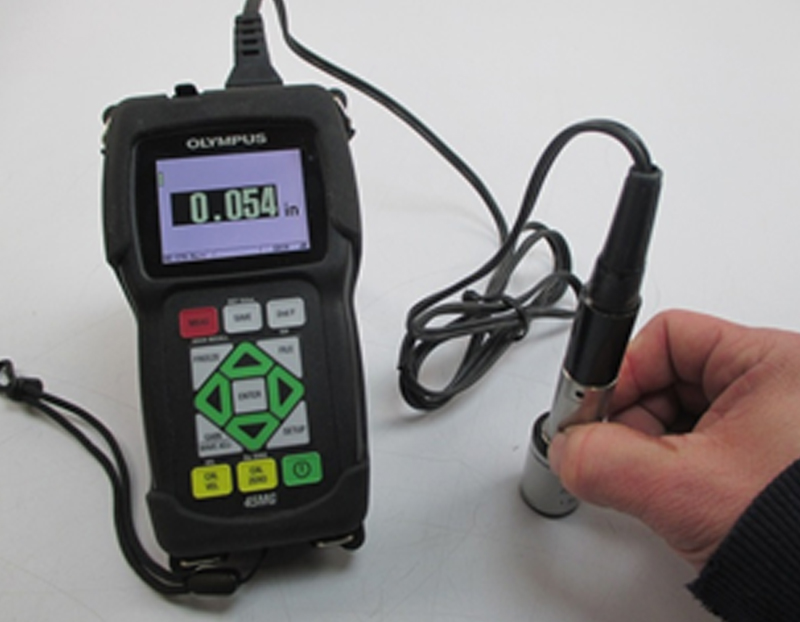

Ultrasonic Thickness Measurement (UTM) is a type of ultrasonic testing that uses high frequency sound waves to measure the thickness of a material. The technique works by transmitting an ultrasonic pulse through the material and measuring the time it takes for the pulse to travel through the material and return to the surface. The thickness of the material can then be calculated based on the speed of sound in the material and the time taken for the pulse to return. UTM is widely used in various industries, including aerospace, shipping, and oil and gas, to monitor the thickness of components and to detect corrosion or other types of material degradation.
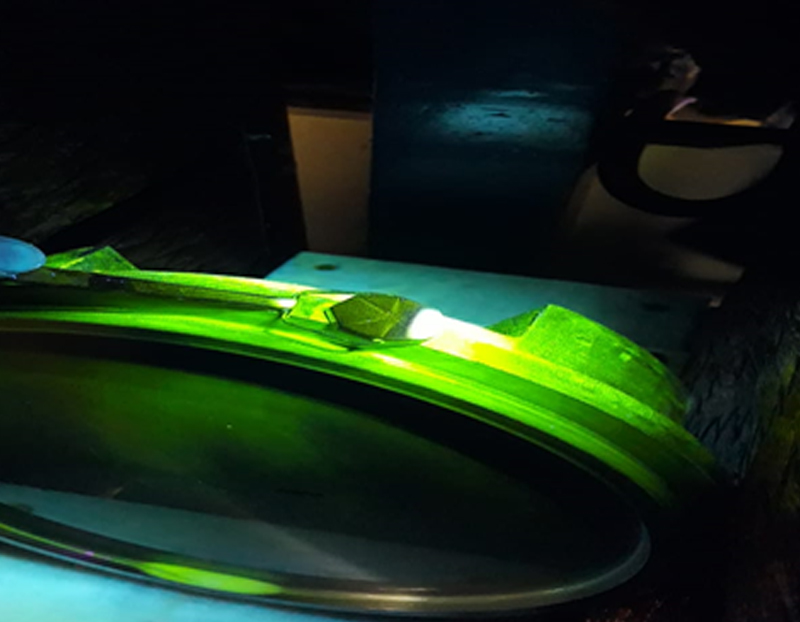

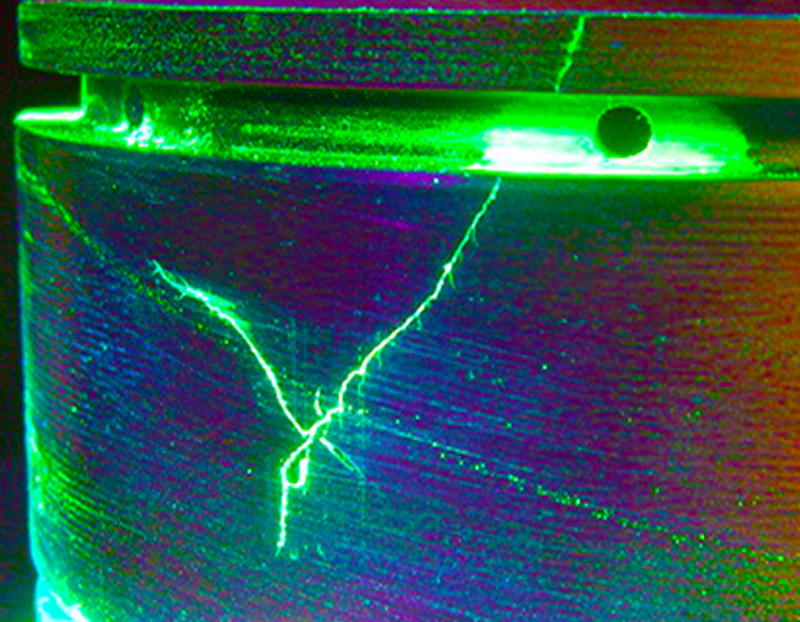
Magnetic Particle Testing (MT) is a non-destructive testing method that detects surface and slightly subsurface discontinuities in ferromagnetic materials. The test is performed by magnetizing the component and then applying magnetic iron oxide or iron oxide-coated magnetic particles to the surface. The magnetic particles are attracted to areas of flux leakage, where they form an easily visible indication of the discontinuity. MT is commonly used to inspect cast iron, forgings, and welds in industries such as aerospace, power generation, and oil and gas. It is a quick and effective method for detecting surface breaking cracks and other surface defects in ferromagnetic materials.
Penetrant Testing (PT), also known as Liquid Penetrant Inspection (LPI), is a non-destructive testing method used to detect surface-breaking flaws in solid non-porous materials such as metals, plastics, and ceramics. The process involves applying a liquid penetrant to the surface of the material, allowing it to penetrate any cracks or surface-breaking flaws, and then removing any excess penetrant. A developer is then applied, which draws penetrant out of the flaws and makes them visible. PT is widely used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and power generation for quality control and safety purposes. It is a simple and effective method for detecting surface defects, and can be performed on a wide range of materials and geometric shapes.
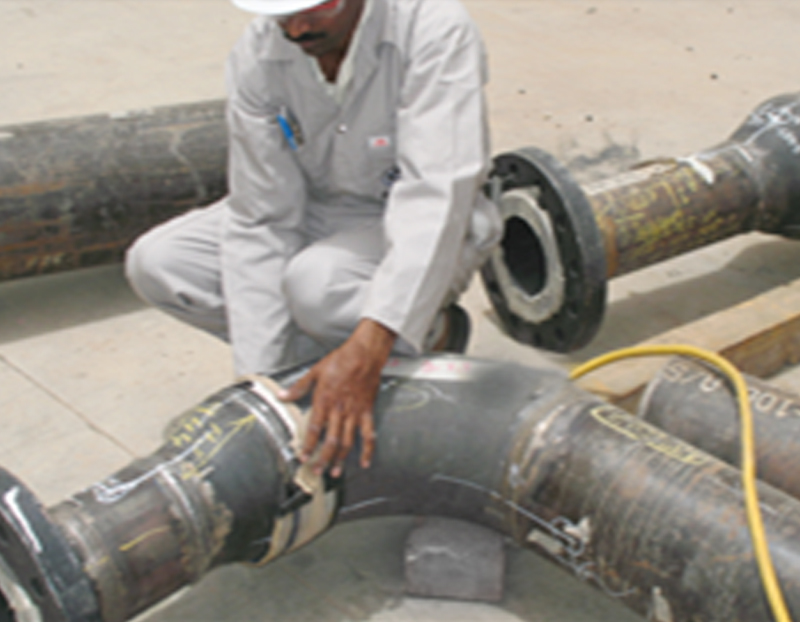

Radiographic Testing (RT), also known as X-ray Testing, is a non-destructive testing method used to inspect the internal structure of solid objects for flaws or anomalies. RT works by passing X-rays or gamma rays through the material and recording the image on a film or digital detector. The X-rays or gamma rays are partially absorbed by the material, and the resulting image shows the internal structure of the object, including any defects or anomalies that may be present. RT is commonly used in industries such as aerospace, power generation, and oil and gas to inspect components for quality control and safety purposes. It is particularly useful for detecting internal flaws in materials that are difficult to inspect using other non-destructive testing methods.
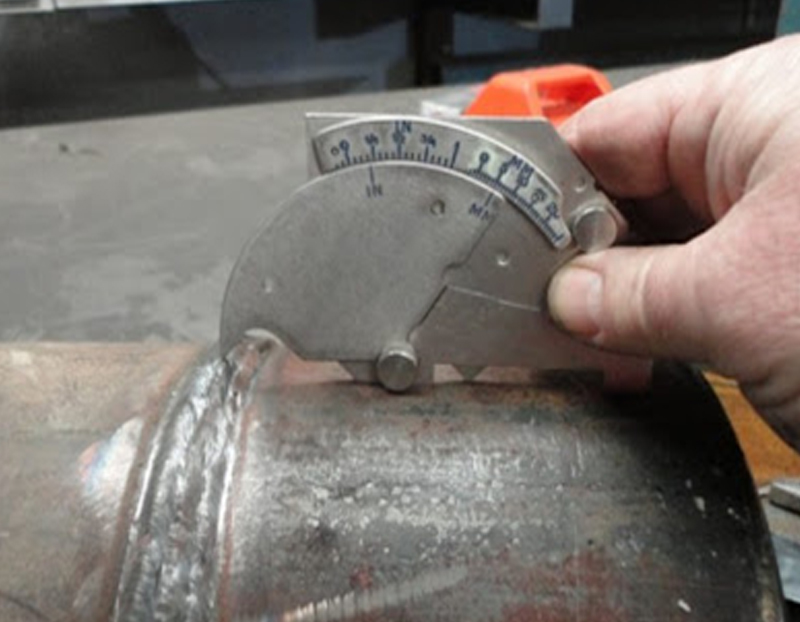

• Inspection performed at low cost in a quick manner.
• Ability to inspect complex sizes and shapes of any material.
• Minimum part preparation required.
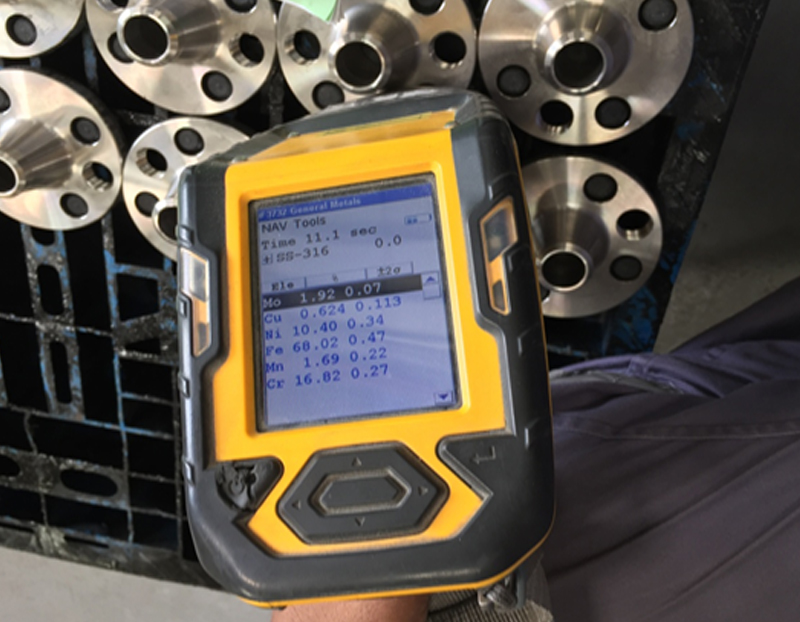

PMI is the analysis of a metallic alloy to demonstrate composition by reading the quantities by percentage of its component elements.
• Isolate finished welds to validate filler material composition and dilution rates.
• Highly specific and accurate results, essential to good quality control.
• Recover lost material traceability.
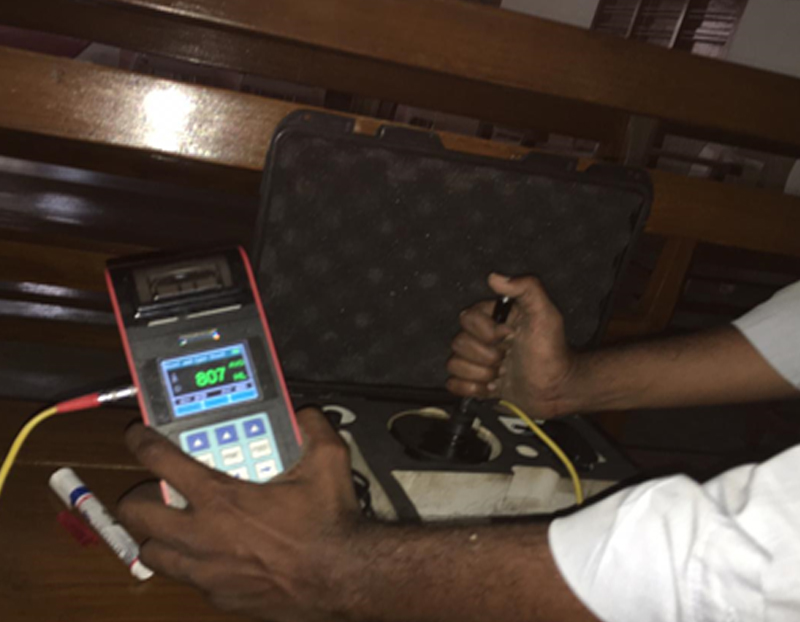

Hardness Testing (HT) is a measure of a material's resistance to permanent indentation or plastic deformation. It is a fundamental mechanical property that provides information about a material's ability to withstand external forces, and is used to evaluate the material's suitability for a specific application. Hardness testing can be performed using a variety of methods. The most common hardness testing methods involve applying a load to a small indentation in the surface of the material and measuring the size of the indentation. HT is widely used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and power generation for quality control and material selection purposes.
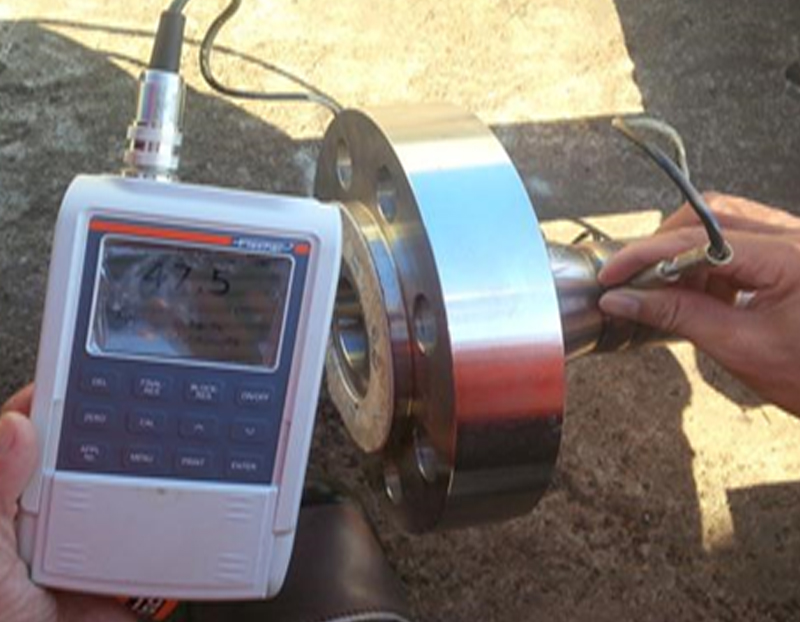

Ferrite testing is a metal with magnetic properties that is present in austenitic stainless steel. The ferrite content in a weld can have an impact on its mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and crack susceptibility. FT can be performed using a variety of methods.
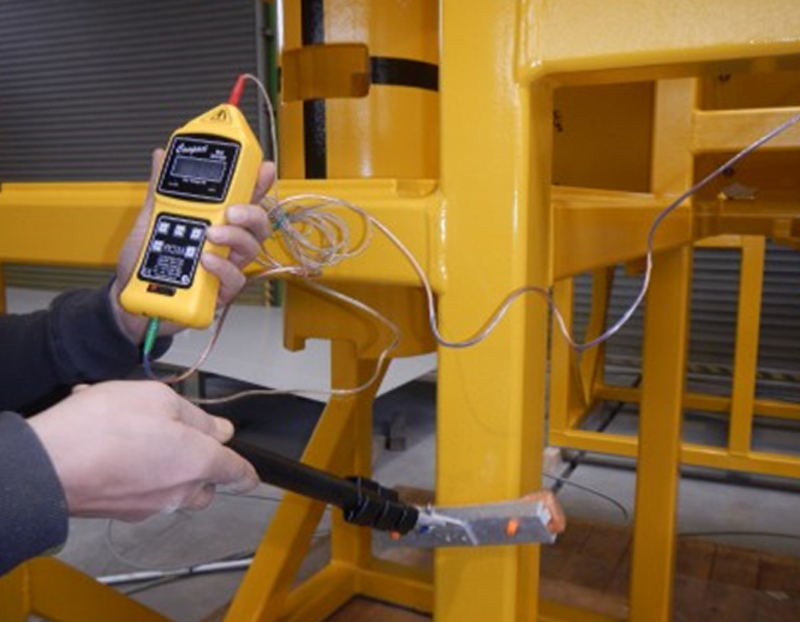

Holiday Inspection is also known as Pinhole Detection used to detect defects or holidays in coatings. A holiday is a term used to describe a gap or break in a coating, which can leave the underlying material exposed to corrosion or other forms of degradations. Holiday inspection is widely used in the pipeline, marine, and coatings industries to ensure the quality and integrity of protective coatings.